A+
monique robles
Add your answer:
In math what does the upside down U mean?
Intersection. This is used in set theory to refer to those members of two sets which are common to both. e.g. the intersection of { p a n s y } and { p r i m u l a } is { p a } In a Venn diagram (a graphical representation of sets) it is the overlap of two shapes.
P and q represents r p q?
tan x
Which algebraic expression represents p plus twice d?
p+2d
Which statement represents the inverse of p → q?
A+
what- Point P represents which of the following?
centroid
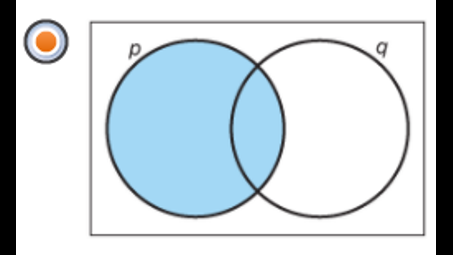
which venn diagram represents -p?
A+
In the equation p m v what does p represent?
in the equation p=m x v, the p represents
What kind of a graphic organizer is most helpful in preparing to write a compare and contrast essay?
A Venn diagram //Apex :p
What is P equals VI?
In electricity, P represents power, V represents voltage, and I represents current. Electric power = Voltage * Current. (P = VI)
Is the p-v diagram is a 3D surface?
yes, the pv diagram is a three dimensional view.
Otto cycle and Diesel cycle with p-v diagram?
165.266
How is it possible to say that area under the curve on pv diagram gives magnitude of the work doen on a gas?
W = F D W = ( F / A ) ( A D ) W = P ( AD ) W = P (V) Work = area under the curve on a P-V diagram.
What represents voltage?
i think it is symbolised with a capital 'e' or 'v' :P hope this helped! :L:L
What does p represent in p equals m times v?
This would be the standard formula for calculating momentum. P represents momentum which is calculated by mass * velocity.
What letter represents voltage?
i think it is symbolised with a capital 'e' or 'v' :P hope this helped! :L:L
Difference between density and specific gravity?
Density is measured by mass per volume and the expressed formula is P=M/V where P represents Density, M represents Mass and V represents Volume. Specific density is a measurement of density relative to another substance and the expressed formula is Substance=P substance/ P reference. An example of specific density is measuring salt in ocean water and comparing it to salt in fresh water.
In math what does the upside down U mean?
Intersection. This is used in set theory to refer to those members of two sets which are common to both. e.g. the intersection of { p a n s y } and { p r i m u l a } is { p a } In a Venn diagram (a graphical representation of sets) it is the overlap of two shapes.
