A mathematical equation, which describes the relationship between pressure (p) of the gaseous adsorbate
and the extent of adsorption at any fixed temperature, is called adsorption isotherm.
The extent of adsorption is expressed as mass of the adsorbate
adsorbed on one unit mass of the adsorbent.
Thus, if x g of an adsorbate
is adsorbed on m g of the adsorbent, then
Extent of adsorption =
z/m
Various adsorption isotherms are commonly employed in describing the adsorption data.
(1) Freundlich
adsorption isotherm
(i) Freundlich
adsorption isotherm is obeyed by the adsorptions where the adsorbate
forms a monomolecular layer on the surface of the adsorbent.
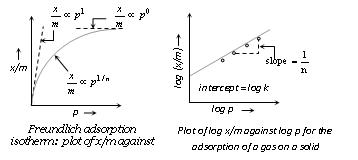
x/m =
kp
1/n (Freundlich
adsorption isotherm) or
log x/m =
log k + 1/n log P
where x is the weight of the gas adsorbed by m gm of the adsorbent at a pressure p, thus x/m represents the amount of gas adsorbed by the adsorbents per gm (unit mass), k and n are constant at a particular temperature and for a particular adsorbent and adsorbate
(gas), n is always greater than one, indicating that the amount of the gas adsorbed does not increase as rapidly as the pressure.
(ii) At low pressure, the extent of adsorption varies linearly with pressure. x/m ∝ p'
(iii) At high pressure, it becomes independent of pressure. x/m ∝ p0
(iv) At moderate pressure x/m depends upon pressure raised to powers x/m ∝ p1/n
(2) The Langmuir - adsorption isotherms
(i) One of the drawbacks of Freundlich
adsorption isotherm is that it fails at high pressure of the gas. Irving Langmuir in 1916 derived a simple adsorption isotherm, on theoretical considerations based on kinetic theory of gases. This is named as Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
(a) Adsorption takes place on the surface of the solid only till the whole of the surface is completely covered with a unimolecular
layer of the adsorbed gas.
(b) Adsorption consists of two opposing processes, namely Condensation of the gas molecules on the solid surface and Evaporation (desorption)of
the gas molecules from the surface back into the gaseous phase.
(c) The rate of condensation depends upon the uncovered (bare) surface of the adsorbent available for condensation. Naturally, at start when whole of the surface is uncovered the rate of condensation is very high and as the surface is covered more and more, the rate of condensation progressively decreases. On the contrary, the rate of evaporation depends upon the covered surface and hence increases as more and more of the surface is covered ultimately an equilibrium will be set up at a stage when the rate of condensation becomes equal to the rate of evaporation (adsorption equilibrium).
(d) The rate of condensation also depends upon the pressure of the gas since according the kinetic theory of gases, the number of molecules striking per unit area is proportional to the pressure.
Mathematically, x/m =
ap/1+bp, where a and b are constants and their value depends upon the nature of gas (adsorbate),
nature of the solid adsorbent and the temperature. Their values can be determined from the experimental data.
Limitation of Langmuir theory(a) Langmuir's theory of unimolecular
adsorption is valid only at low pressures and high temperatures.
(b) When the pressure is increased or temperature is lowered, additional layers are formed. This has led to the modern concept of multilayer adsorption.
What else can I help you with?
What is the difference between the Freundlich BET and Langmuir adsorption isotherms?
There are a few differences, but the main one is that Langmuir can only be used for surfaces which are cover by only one layer of gas and the BET surface area is calculated using the multilayer model.
What happens when a cloud burst?
Cloudbursts descend from very high clouds, sometimes with tops above 15 kilometers. Meteorologists say the rain from a cloudburst is usually of the shower type with a fall rate equal to or greater than 100mm (3.94 inches) per hour. During a cloudburst, more than 2 cm of rain may fall in a few minutes. When there are instances of cloudbursts, the results can be disastrous. Rapid precipitation from cumulonimbus clouds is possible due to so called Langmuir precipitation process in which large droplets can grow rapidly by coagulating with smaller droplets which fall down slowly.
What is the difference between the Freundlich BET and Langmuir adsorption isotherms?
There are a few differences, but the main one is that Langmuir can only be used for surfaces which are cover by only one layer of gas and the BET surface area is calculated using the multilayer model.
What is Freundlich adsorption isotherm and Langmuir isotherm?
At a given temperature, the extent of adsorption will increase with the increase of pressure of the gas. The extent of adsorption is measured as x/m, where mi= is the mass of adsorbent and x that of adsorbate. At low pressure, x/m varies linearly with p. As per Freundlich adsorption equation Taking log both sides of the equation, we get, At low pressure, x/m=kP At high pressure, x/m=kPo This is called Freundlich adsorption isotherm at a constant temperature. Freundlich isotherm fails at high pressure and is only for physical adsorption. Langmuir isotherm is represented as x/m=ap/(1+bp) (a and b are constants) At very high pressure,(bp>>1) x/m=a/b At very low pressure,(bp<<1) x/m=ap
How do you calculate molecular weight of a compound from its langmuir isotherm?
The monolayer capacity of the adsorbent is equal to number of moles of adsorption sites present on one gram of sample. The Langmuir and BET isotherms may be used to find th monolayer capacity of the adsorbent. Thus on taking the reciprocal of the monolayer capacity, one can find the molecular weight of the adsorbent.
Is irving langmuir poor or rich?
As we known, Ivring Langmuir is poor, but he paid great contribute to adsorption determination, especially the Langmuir surface area. By GOLD APP INSTRUMENTS.
What is difference between BET and Langmuir surface area?
BET surface area testing principle is from 3 men names, Langmuir is from one. Usually BET surface area mean multi-layer adsorption, but Langmuir refers to monolayer adsorption. BET surface area principle reflects the real adsorption situation an process for most materials, so, be treated more important and trustable than Langmuir surface area. There area some analyzers( e.g. V-Sorb 2800S, V-Sorb 4800) can test both BET and Langmuir, also with pore size related, you can ask from them for a free test, because our insitutes got one already.
How do you calculate KL in langmuir isotherm?
To calculate the Langmuir constant (KL) in the Langmuir isotherm model, you typically perform a nonlinear regression analysis on experimental data using the Langmuir equation: (q = \frac{{q_{max} K_L C}}{{1 + K_L C}}), where q is the adsorption capacity at a given concentration C, and (q_{max}) is the maximum adsorption capacity. The Langmuir constant (KL) can be determined by fitting the experimental data to this equation and solving for KL.
What did langmuir fisher invent?
Langmuir and Fisher are two separate scientists who made significant contributions in different fields. Irving Langmuir was a chemist and physicist known for his work on surface chemistry and plasma physics, while Ronald Fisher was a statistician known for his contributions to the field of statistics, particularly in experimental design and hypothesis testing. Langmuir developed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, and Fisher developed the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the design of experiments.
What is hill isotherm?
The Langmuir equation (also known as the Langmuir isotherm, Langmuir adsorption equation or Hill-Langmuir equation) relates the coverage or adsorption of molecules on a solid surface to gas pressure or concentration of a medium above the solid surface at a fixed temperature.
Why did Irving Langmuir win The Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1932?
Irving Langmuir won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1932 for his work in surface chemistry, specifically his studies of monolayer films and surface phenomena. His research on adsorption and surface reactions laid the foundation for understanding surface properties and catalysis.
What should be result of adsorption acetic acid on charcoal?
The acetic acid molecules will be attracted to the surface of the charcoal due to adsorption, leading to their accumulation on the charcoal's surface. This process can be used to remove acetic acid from a solution through physical adsorption without undergoing a chemical reaction.
When did Gavin I. Langmuir die?
Gavin I. Langmuir died in 2005.
When was Gavin I. Langmuir born?
Gavin I. Langmuir was born in 1924.