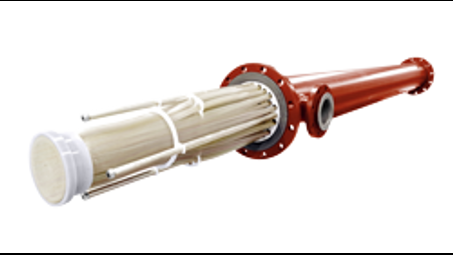
shell and tube heat exchangers are used mostly in the chemical processing industry for heating, cooling, condensing, and evaporating highly corrosive liquids and gases.
AMETEK Fluoropolymer Product shell and tube heat exchanger was the first heat exchanger developed using fluoropolymer tubes and the patented honeycomb tube to tube sheet joint which has been successfully used for over 55 years.
Sulfuric Acid is the chemical most used with Ametek Fpp heat exchangers. The process of making sulfuric acid can vary, but any company dealing with the manufacturing process has a high potential for the use of a fluoropolymer heat exchanger in their process.
Other Acids commonly requiring fluoropolymer heat exchangers are Hydrochloric, Nitric and Hydrofluoric Acids. Another chemical manufacturing industry fluoropolymer heat exchangers are used in is the Chlor-Alkali manufacturing process.
What else can I help you with?
What are fireworks shot out of?
The only ones that need to be fired 'out-of-something' are rockets (use a tube that the stick fits into) and aerial shells. Aerial shells need to fired from a mortar tube which is a card, plastic, fibreglass or metal tube that has the same inside diameter as the shell to be launched.
Will a sea star be able to eat clams without using its tube feet. Explain?
No, sea stars use their tube feet to pry open the clam's shell and then evert their stomach into the clam to digest its soft tissues. Without the use of tube feet, the sea star would not be able to access the clam's flesh to consume it.
What is the safest way to heat up a flammable liquid in a test tube?
The safest way to heat up a flammable liquid in a test tube is to use a water bath or a heating mantle to provide indirect heat. Never use a direct flame, as this can lead to ignition of the flammable liquid. Ensure proper ventilation and keep a fire extinguisher nearby as a precaution.
Why can't you heat a test tube with a stopper in it?
You shouldn't heat a test tube with a stopper in it because the heat can cause the contents to expand and produce gas, leading to increased pressure inside the closed system. This pressure can build up to the point where the stopper may pop out violently or the test tube could break, posing a safety risk. Always use an open container for heating to allow for safe gas escape.
Heating Conduction where it is used?
In computer heatsinks the heat of the CPU chip is conducted to the heatsinks (which then use convection to shed excess heat). In an electric stove the coil is heated up and the heat is conducted to the cookware you put on it.
What is the different between plate heat exchangers and tube heat exchangers?
Plate heat exchangers use flat plates to transfer heat between two fluids, providing a large surface area for efficient heat transfer in a compact design. Tube heat exchangers utilize tubes to facilitate heat exchange between fluids, offering a more traditional and versatile approach to heat transfer applications. Plate heat exchangers are typically more efficient and cost-effective for certain applications compared to tube heat exchangers.
What is bundle factor in shell and tube condenser?
The bundle factor in a shell and tube condenser refers to the effectiveness of the tube bundle in promoting heat transfer between the fluids. It is defined as the ratio of the actual heat transfer area provided by the tube bundle to the theoretical heat transfer area if all tubes were completely utilized. A higher bundle factor indicates better use of the available tube area, resulting in improved thermal performance and efficiency of the condenser. This factor is crucial for optimizing design and operational parameters in heat exchangers.
How many types of heat exchangers are there?
Heat exchangers are devices that allow heat to be transferred between two or more fluids of different temperatures (vapors, liquids, or gases). The heat transfer process can be liquid-to-gas, gas-to-gas, or liquid-to-liquid, and it can happen through a solid separator or direct fluid contact, depending on the type of heat exchanger used. Other design features, such as construction materials and components, heat transfer processes, and flow configurations, aid in classifying and categorizing the various types of heat exchangers accessible. Heat exchanger makers offer a wide range of heat exchanging devices designed and manufactured for use in both cooling and heating processes and find applications across a wide range of industries. This blog examines the numerous types and designs of heat exchangers, as well as their functions and mechanics. This blog also discusses the factors to consider when choosing a heat exchanger and the most popular applications for each one.
Disadvantages of shell and tube heat exchanger?
it is difficult to remove the scales. we cannot use scale forming fluid through the shell because if we pass, the scales are formed and it corrodes the shell.
Why most of the heat exchangers are made use of forced convection?
Better heat transfer than natural convection. When compared to water or liquid cooled heat exchangers, the argument could be made that air is a cheaper cooling medium.
Why Don't we use odd number of tube passes in Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger?
It is difficult from cleaning point of view. Both end chambers have to be removed so as to clean the heat exchanger with odd nos of passes. Thanks & Regards Priyanka Karkera
How are tube heat exchangers designed?
Tube-type heat exchangers are designed using tubes to contain and convey either the exchange medium or that which needs heating or cooling. Let's look at an example and it will be more clear. In a condenser below a steam turbine, the "used steam" comes out of the turbine and passes across many tubes through which cool water is being pumped. The steam condenses into water as heat is exchanged with the tubes, which were cooled by the water being pumped through them. Use the link (provided) to the Wikipedia article on the surface condenser for some great drawings and a more detailed explanation.
Why do we use test tube?
we use test tube to hold chemicals and heat and chemicals.
Heat Exchanger Types and Uses?
heat sink classified according to the shape, the shape is how to dissipate within the selected heat sink that is the main intension here,, k type l type rectangular triangular chassis i know this much u can down load the pdfs for the types how to select the required heat sink 9844354439
What is AEM type heat Exchanger?
I'm just concluding a work in which I had to design a shell and tube exchanger for condensation of a mixture of gases and vapor at low pressure. That was the type I chose. AEM is a type of shell and tube heat exchanger, according to TEMA standards. They use 3 letters to describe the configuration of the heat exchanger. First letter refers to the front head, second letter to the shell type and third letter to the rear end stationary head. So in this case, with a type A you would have: A for channel and easily removable cover. E as it is a one pass shell and M because you have a fixed tubesheet with a rear end in bonnet shape.
Q: What industries commonly use Admiralty Brass Tubes?
A: Admiralty Brass Tubes are widely used in heat exchangers and condensers in power plants and refineries.
What equipment do you use when heating a test tube over a Bunsen burner?
When heating a test tube over a Bunsen burner, you typically use heat-resistant gloves to handle the test tube, a test tube holder to hold the test tube, and a Bunsen burner for heating. It's also important to have a heat-resistant mat or pad to place the test tube on while heating.
